-

Study on Precision Polishing Technology Combining Electrophoresis and Magnetic Finishing
Lieh-Dai Yang,
Kun-Ling Wu,
Chin-Chang Yeh,
Hsin-Min Lee
Issue:
Volume 5, Issue 6, November 2016
Pages:
235-240
Received:
16 October 2016
Published:
17 October 2016
Abstract: The aim of this paper is to improve the quality of surface roughness of precision molds, which is difficult to control in the traditional polishing technology, and to provide a kind of equipment which is simple and easy to operate in orderto obtain a high precision in surface finishing and polishing. The combination of magnetic force polishing and electrophoretic polishing is mainly to combine the magnetic grinding mechanism with the electrophoretic deposition method to conduct finishing and polishing experiments. From the experimental results we can see that the combination of magnetic force and electrophoretic polishing can make the original roughness of the discharge surface of 1.7μm down to 0.08μm which is mirror effect after improving for 20 minutes. The experimental results show that the precision polishing combined with electrophoresis and magnetic grinding can effectively improve the surface roughness and therefore reduce technical and personnel training costs, shorten the production cycle time, and thus improve production efficiency. It can be concluded as a quite competitive technology in the industry.
Abstract: The aim of this paper is to improve the quality of surface roughness of precision molds, which is difficult to control in the traditional polishing technology, and to provide a kind of equipment which is simple and easy to operate in orderto obtain a high precision in surface finishing and polishing. The combination of magnetic force polishing and ...
Show More
-

Optimal Machining Parameters of EDM in Gas Based on Response Surface Methodology
Yan-Cherng Lin,
Han-Ming Chow,
Yuan-Feng Chen,
Jia-Feng Liu
Issue:
Volume 5, Issue 6, November 2016
Pages:
241-247
Received:
18 October 2016
Published:
19 October 2016
Abstract: This paper aims to establish an effective mathematical model with relation to electrical discharge machining (EDM) in gas based on response surface methodology (RSM). Moreover, the optimal combination levels of machining parameters for material removal rate (MRR) and surface roughness (SR) were also explored. The experimental tasks were implemented by a specific design of experimental method named central composite design (CCD) method based on RSM to develop quadratic regression mathematical model. The significant parameters and their interactions were examined by analysis of variance (ANOVA) to evaluate the importance on MRR and SR. The essential parameters of EDM in gas such as peak current (Ip), pulse duration (Tp), air pressure (GP) and servo reference voltage (Sv) were chosen to investigate the effects on MRR and SR. From the analysis results, the optimal set of parameter setting levels were 12 A peak current (Ip), 750 μs pulse duration (Tp), 5 kg/cm2 gas pressure (GP) and 34 V servo reference voltage (Sv), and the optimization of MRR and SR were 1.99 mm3 and 2.43μm as the machining parameters were set at the optimal levels.
Abstract: This paper aims to establish an effective mathematical model with relation to electrical discharge machining (EDM) in gas based on response surface methodology (RSM). Moreover, the optimal combination levels of machining parameters for material removal rate (MRR) and surface roughness (SR) were also explored. The experimental tasks were implemented...
Show More
-

A Study on the Effects of Material to Liquor Ratio on the Colorfastness of Synolon Yellow EXW Fluorescent Disperse Dye
Azizul Islam,
Rashaduzzaman,
Mahbubur Rahman,
Jagannath Biswas,
Elias Khalil
Issue:
Volume 5, Issue 6, November 2016
Pages:
248-253
Received:
11 September 2016
Accepted:
21 September 2016
Published:
20 October 2016
Abstract: This study highlighted the influence of change in material to liquor ratio on the colorfastness properties of Synolon Yellow EXW fluorescent disperse dye applied on knitted polyester fabric in exhaust dyeing method. Three different liquor ratios (1:6, 1:8 and 1:10) were used and dye shade percentages were 0.5%, 1.0% and 1.5%. The results showed that an increment in liquor ratios increased the colorfastness to washing (color change) for the shade percentages of 0.5 and 1.5. Wash fastness (color staining) grading was not satisfactory when material to liquor ratio is 1:6. Increasing the amount of liquor resulted least color bleeding. No color fading has been observed in dry rubbing test for 1:10 material to liquor ratio. Increment in the material to liquor ratios resulted better dry and wet rubbing fastness for both color change and color staining. Variation in the liquor ratios showed no effects on the abrasion resistance property.
Abstract: This study highlighted the influence of change in material to liquor ratio on the colorfastness properties of Synolon Yellow EXW fluorescent disperse dye applied on knitted polyester fabric in exhaust dyeing method. Three different liquor ratios (1:6, 1:8 and 1:10) were used and dye shade percentages were 0.5%, 1.0% and 1.5%. The results showed tha...
Show More
-

Effects of Water Hardness on Dyeing of Cotton Fabrics with Different Types of Reactive Dyes and Shade Percentages
Mahbubur Rahman,
Azizul Islam,
Jagannath Biswas
Issue:
Volume 5, Issue 6, November 2016
Pages:
254-260
Received:
11 September 2016
Accepted:
21 September 2016
Published:
27 October 2016
Abstract: This research was investigated the influence of water hardness on dyeing of cotton fabric with three types of reactive dyes (Synozol, Ramazol and Setazol). The effects of various fastness (color fastness to wash, abrasion test, Rubbing test and Perspiration test) properties of dyes were also studied and reported in this paper in details. Single color (Blue) is used for the shade of 1% and 2% and varied water hardness of 120 ppm, 70 ppm and 9 ppm respectively. The main objective of this paper was to find out the parameters of various fastness properties at different range of water hardness in the application of different types of reactive dyes. It is visualized that different amount of water hardness showed in different fastness for using three types of reactive dyes having shade of 1% and 2%. We reported that water hardness up to 9 ppm, for using three types of reactive dyes showed excellent wash fastness and it deteriorates with increasing hardness. Setazol 1% & 2%, showed highest abrasion resistance at 9 ppm water hardness compare to other dyes at higher water hardness. Rubbing test result also showed very good for 9 ppm water hardness in three reactive dyes irrespective of shade percentage. The perspiration test result is good at 9 ppm water hardness for all types of reactive dyes with all shade percentages.
Abstract: This research was investigated the influence of water hardness on dyeing of cotton fabric with three types of reactive dyes (Synozol, Ramazol and Setazol). The effects of various fastness (color fastness to wash, abrasion test, Rubbing test and Perspiration test) properties of dyes were also studied and reported in this paper in details. Single col...
Show More
-

Influence of Thiourea Concentration on Some Physical Properties of Chemically Sprayed Cu2ZnSnS4 Thin Films
Nabeel A. Bakr,
Ziad T. Khodair,
Hussein I. Mahdi
Issue:
Volume 5, Issue 6, November 2016
Pages:
261-270
Received:
28 September 2016
Accepted:
7 October 2016
Published:
1 November 2016
Abstract: In this work Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) films were deposited by using chemical spray pyrolysis (CSP) technique at substrate temperature of (400 ± 10) °C and thickness of about (300 ± 10) nm at different Thiourea Concentrations of (0.14, 0.16, 0.18, 0.20, 0.22 and 0.24) M. Copper chloride (CuCl), zinc chloride (ZnCl2), tin chloride (SnCl4.5H2O) and thiourea (SC(NH2)2) were used as sources of copper ions, zinc ions, tin ions and sulfur ions respectively. The structural, morphological and optical properties of these films have been studied using XRD, AFM, and UV-Visible spectroscopy respectively. The XRD results showed that all films are polycrystalline in nature with tetragonal structure and preferred orientation along (112) plane. The crystallite size (Dav) of all samples was calculated using Scherrer’s equation and it is found that the sample deposited at thiourea concentration of 0.20 M has maximum crystallite size of 31.25 nm, while it was minimum (18.02 nm) for the sample prepared at thiourea concentration of 0.16 M. The AFM results showed smooth and homogenous thin films. The optical energy band gap (Eg) for allowed direct electronic transition was calculated using Tauc’s plot. It is found that the energy band gap (Eg) decreases as the thiourea concentration increases and it was in the range of (2.22 - 1.75) eV. Urbach energy, refractive index, extinction coefficient and dielectric coefficient of all deposited films were estimated and the results were discussed.
Abstract: In this work Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) films were deposited by using chemical spray pyrolysis (CSP) technique at substrate temperature of (400 ± 10) °C and thickness of about (300 ± 10) nm at different Thiourea Concentrations of (0.14, 0.16, 0.18, 0.20, 0.22 and 0.24) M. Copper chloride (CuCl), zinc chloride (ZnCl2), tin chloride (SnCl4.5H2O) and thiourea (...
Show More
-

Effects of Pulverized Fuel Ash and Condensed Silica Fume on Heat Generation of Curing Concrete
J. J. Chen,
H. N. Chen,
L. G. Li
Issue:
Volume 5, Issue 6, November 2016
Pages:
271-276
Received:
4 November 2016
Published:
5 November 2016
Abstract: The heat generated during the curing period of concrete may results in early thermal cracking. To avoid or at least alleviate this early thermal cracking problem, replacing part of cement by cementitious materials should be an effective method. Herein, it is proposed to add PFA or CSF as cement replacement to lower the cement content and heat generated from the hydration of cement. To study the effectiveness of adding PFA or CSF in reducing the heat generation of curing concrete, a series of concrete mixes with water/cement ratios ranging from 0.24 to 0.40 and different amounts of PFA or CSF added were tested for their heat generation. The results illustrated that the addition of PFA or CSF as cement replacement could effectively reduce the adiabatic temperature rise and heat generation of curing concrete, while the addition of CSF is much more effectively than addition of PFA in reducing heat generation at the same strength.
Abstract: The heat generated during the curing period of concrete may results in early thermal cracking. To avoid or at least alleviate this early thermal cracking problem, replacing part of cement by cementitious materials should be an effective method. Herein, it is proposed to add PFA or CSF as cement replacement to lower the cement content and heat gener...
Show More
-

Hypereutectic Al-Si Alloy with Completely Nodular Eutectic Silicon: Microstructure and Process
Issue:
Volume 5, Issue 6, November 2016
Pages:
277-283
Received:
27 September 2016
Accepted:
11 October 2016
Published:
9 November 2016
Abstract: The achievement of hypereutectic Al-Si alloys with completely nodular eutectic Si has been studied. The procedure contained two steps: firstly, achieving hypereutectic direct electrolytic Al-Si alloys (HDEASA) with completely eutectic structure and secondly, spheroidizing eutectic Si upon soaking. HDEASAs with Si level in the range from 13.2 wt% to 17.6 wt% were made from direct electrolytic eutectic Al-Si alloy ingot and Al-50 wt% Si hardener. As cast microstructure of HDEASA was composed of primary-free quasi-eutectic cells. In comparison with commercial alloys, the lower heating temperature of 505°C -515°C for 4-8 hrs was required to fully spheroidize Si crystal, either fine fibrous or even flaky in casting. Most of the spheres ranged in size from 1.0μm to 4.0μm. Many measurements were focused on the variety of Si phase size in eutectic cells against the distance from the center of the cells. The origin of granulation of primary-free quasi-eutectic Si crystal is associated with its thermodynamic structural instability, accompanied by crystallographic defects, related to the electrolytic process.
Abstract: The achievement of hypereutectic Al-Si alloys with completely nodular eutectic Si has been studied. The procedure contained two steps: firstly, achieving hypereutectic direct electrolytic Al-Si alloys (HDEASA) with completely eutectic structure and secondly, spheroidizing eutectic Si upon soaking. HDEASAs with Si level in the range from 13.2 wt% to...
Show More
-

Photoluminescence and Energy Transfer Between Sm 3+ Ions in LaF3 Nanocrystals Prepared by Hydrothermal Method
Hoang Manh Ha,
Tran Thi Quynh Hoa,
Le Van Vu,
Nguyen Ngoc Long
Issue:
Volume 5, Issue 6, November 2016
Pages:
284-289
Received:
10 October 2016
Accepted:
19 October 2016
Published:
9 November 2016
Abstract: The aim of this research is to study photoluminescent properties and particularly energy transfer between Sm3+ ions in LaF3 nanocrystals because the energy transfer process has a significant effect on the luminescence efficiency and lifetime. Sm3+-doped LaF3 nanocrystals with 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0 and 5.0 mol% Sm3+ have been prepared by hydrothermal method. The obtained nanocrystals were characterized by X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy, photoluminescence and luminescence decay measurement. The results showed that the LaF3:Sm3+ nanocrystals possess hexagonal structure with 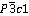 space group. The room temperature photoluminescence and photoluminescence excitation spectra of LaF3:Sm3+ were investigated in detail and interpreted by optical intra-configurational f–f transitions within Sm3+ ions. When Sm3+ ion concentration in the nanocrystals is increased, the excitation energy is transferred from the “bulk” Sm3+ ions to the surface Sm3+ ions followed by non-radiative recombination at centers at the surface of the nanocrystals. The photoluminescence decay curves of 593 nm peak in the LaF3 nanocrystals doped with 1.0-5.0 mol% Sm3+ were best fitted to the Inokuti-Hirayama model with the dominant dipole-quadrupole interaction (S = 8). The values of fitting parameters for the energy transfer process were determined.
Abstract: The aim of this research is to study photoluminescent properties and particularly energy transfer between Sm3+ ions in LaF3 nanocrystals because the energy transfer process has a significant effect on the luminescence efficiency and lifetime. Sm3+-doped LaF3 nanocrystals with 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0 and 5.0 mol% Sm3+ have been prepared by...
Show More
space group. The room temperature photoluminescence and photoluminescence excitation spectra of LaF3:Sm3+ were investigated in detail and interpreted by optical intra-configurational f–f transitions within Sm3+ ions. When Sm3+ ion concentration in the nanocrystals is increased, the excitation energy is transferred from the “bulk” Sm3+ ions to the surface Sm3+ ions followed by non-radiative recombination at centers at the surface of the nanocrystals. The photoluminescence decay curves of 593 nm peak in the LaF3 nanocrystals doped with 1.0-5.0 mol% Sm3+ were best fitted to the Inokuti-Hirayama model with the dominant dipole-quadrupole interaction (S = 8). The values of fitting parameters for the energy transfer process were determined.
Abstract: The aim of this research is to study photoluminescent properties and particularly energy transfer between Sm3+ ions in LaF3 nanocrystals because the energy transfer process has a significant effect on the luminescence efficiency and lifetime. Sm3+-doped LaF3 nanocrystals with 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0 and 5.0 mol% Sm3+ have been prepared by...
Show More
-

Processing Characteristics Exploration of Metal Based Diamond Wheel of WEDM Dressing and Truing
Han-Ming Chow,
Lieh-Dai Yang,
Yan-Cherng Lin,
Jung-Chou Hung,
Yao-Zhong Gu
Issue:
Volume 5, Issue 6, November 2016
Pages:
290-296
Received:
9 November 2016
Published:
10 November 2016
Abstract: This study aims to conduct experiments to explore metal based diamond wheel dressing and truing using developed wire electrical discharge (WEDM). The experimental outputs were analyzed to evaluate the effects of machining parameters on machining removal rate (MRR) and abrasive protrusion during dressing and truing caused by WEDM. During experiments, the wear and compensation issues could be overcome induced by the traditional EDM to improve the efficiency and precision as the WEDM was adopted. The experimental results showed as expected that the wire discharge grinding wheel dressing will lead the processing base not offset. In Taguchi experiment the maximum contribution was current and pulse time, large diameter grinding wheel to remove the highest rate of 11.78 mm3/min, while maximum protrusion amount only 33.12 μm, can reach the theoretical maximum protrusion amount.
Abstract: This study aims to conduct experiments to explore metal based diamond wheel dressing and truing using developed wire electrical discharge (WEDM). The experimental outputs were analyzed to evaluate the effects of machining parameters on machining removal rate (MRR) and abrasive protrusion during dressing and truing caused by WEDM. During experiments...
Show More
-

Improvement of Chemical and Thermal Properties of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) by Using Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs)
Eman Mohammed Khalaf,
Sameer Ahmed Awad
Issue:
Volume 5, Issue 6, November 2016
Pages:
297-301
Received:
15 October 2016
Accepted:
14 November 2016
Published:
17 December 2016
Abstract: This work aims to investigate the improvements of thermal and chemical properties of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) by using Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs). MWCNT were used as a reinforcement in polyethylene terephthalate with different weight percentages (0.1, 0.5, and 1) % respectively. The direct mixing process was used to prepare (polyethylene terephthalate / MWCNTs) composites. The ultrasonic mixing technique was applied to disperse the MWCNTs material into polyethylene terephthalate. The intensities of absorption of hydroxyl and carbonyl group decreased with increasing the addition of MWCNTs from (0.1-1%), comparing with pure PET. The results of TGA showed that the incorporation of MWCNTs into pure PET slightly improves the thermal stability because interfaces between multifuntionlized MWCNTs and pure PET causes of reducing brittle behavior and increased due to the high crosslinking of pure PET. The mechanical tests appeared significant improvements with increasing of MWCNTs concentrations. The SEM micrographs showed more voids between the pure PET chains before adding MWCNTs while MWCNTs-PET composites appeared more homogeneous, crosslink density and less voids between the chains.
Abstract: This work aims to investigate the improvements of thermal and chemical properties of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) by using Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs). MWCNT were used as a reinforcement in polyethylene terephthalate with different weight percentages (0.1, 0.5, and 1) % respectively. The direct mixing process was used to prepare (pol...
Show More
-

Comprehensive Characterization of Lignocellulosic Fruit Fibers Reinforced Hybrid Polyester Composites
B. NagarajaGanesh,
R. Muralikannan
Issue:
Volume 5, Issue 6, November 2016
Pages:
302-307
Received:
7 October 2016
Accepted:
3 November 2016
Published:
18 December 2016
Abstract: This work is focused to fabricate and characterize hybrid polyester composites containing equal weight percentages of lignocellulosic fruit fibers namely Cocos nucifera and Luffa cylindrica. Samples with four different compositions (10%, 20%, 30%, and 40%) containing random fiber orientation are fabricated using handlayup technique and their effect on the flexural strength and impact strength is studied and compared with their individual counterparts. Enhanced mechanical properties are obtained when the combined weight percentage of both fibers is 30% by weight. This hybrid composite sample is characterized by Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction and Thermogravimetric analysis. Surface morphology of the fractured sample with elemental analysis is studied using scanning electron microscope and Energy Dispersive Analysis of X-rays. FTIR peaks confirm the presence of biopolymers cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin. The thermogram confirms the presence of lignin, an amorphous hydrophobic biopolymer with strong intermolecular, intramolecular hydrogen bond and cross linking of the molecules requiring more energy to breakdown resulting in good thermal stability of the hybrid composites around 200°C. Elemental analysis gives O/C ratio of 0.45 corroborating the lignin presence at the surface.
Abstract: This work is focused to fabricate and characterize hybrid polyester composites containing equal weight percentages of lignocellulosic fruit fibers namely Cocos nucifera and Luffa cylindrica. Samples with four different compositions (10%, 20%, 30%, and 40%) containing random fiber orientation are fabricated using handlayup technique and their effect...
Show More










