In order to reduce the risk of large-scale thermal recovery of heavy oil in Bohai Oilfield, L Oilfield is selected to carry out horizontal well steam stimulation pilot tests. Previous studies have summarized the rationality of the injection parameters and initial production characteristics of this experiment, but the evaluation of its development effectiveness is still blank. Based on the study of the decline law of A23H well cold recovery using reservoir engineering methods, this article evaluates the initial production capacity, production increase effect, technical recoverable reserves, and throughput cycles of steam stimulation. The results show that the thermal recovery production of steam stimulation is three times that of cold recovery, which can significantly improve the production capacity of a single well. The initial daily oil production of two wells is 74m3/d and 90m3/d, respectively, which is 3.0 times and 3.6 times that of the initial production of cold recovery, exceeding the design level of the reservoir; The first round has the best yield increase effect, with an average daily oil increase of 31m3/d, and gradually decreasing thereafter. By the fifth round, it was only 13m3/d. In terms of yield increase multiples, each round can reach about 2 times; The technically recoverable reserves are 19.03 × 104m3, requiring 8-9 rounds. Through this performance evaluation, we have strengthened our confidence in promoting the application of steam injection technology in Bohai Oilfield to achieve large-scale thermal recovery.
| Published in | Science Discovery (Volume 12, Issue 3) |
| DOI | 10.11648/j.sd.20241203.13 |
| Page(s) | 54-57 |
| Creative Commons |
This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, provided the original work is properly cited. |
| Copyright |
Copyright © The Author(s), 2024. Published by Science Publishing Group |
Heavy Oil, Steam Throughput, Pilot Test, Effect Evaluation, Bohai Oilfield
井号 | 轮次 | 第二轮 | 第三轮 | 第四轮 | 第五轮 | |
A22H | 生产时间 | 天 | 310 | 520 | 296 | 375 |
累产油 | 方 | 10625 | 19119 | 6309 | 6774 | |
平均日产油 | 方/天 | 34 | 37 | 21 | 18 | |
A23H | 生产时间 | 天 | 323 | 331 | 254 | 680 |
累产油 | 方 | 8216 | 8860 | 6402 | 14179 | |
平均日产油 | 方/天 | 25 | 27 | 25 | 21 |
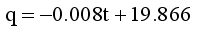 (1)
(1) 轮次 | 第一轮 | 第二轮 | 第三轮 | 第四轮 | 第五轮 | |
热采累产油 | m3 | 12003 | 8603 | 7852 | 6062 | 5327 |
热采平均日产油 | m3/d | 47 | 34 | 31 | 28 | 21 |
冷采预测累产油 | m3 | 4005 | 3488 | 2972 | 2113 | 2019 |
冷采平均日产油 | m3/d | 15.8 | 13.7 | 11.7 | 9.8 | 7.9 |
热采累增油 | m3 | 7998 | 5115 | 4880 | 3949 | 3308 |
热采平均日增油 | m3/d | 31 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 13 |
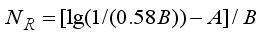 (2)
(2) 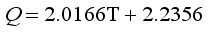 (3)
(3) 轮次 | 第一轮 | 第二轮 | 第三轮 | 第四轮 | 第五轮 | |
累积注入量 | m3 | 7501 | 16956 | 27526 | 39744 | 53544 |
累积采出量 | m3 | 5290 | 12305 | 20733 | 29943 | 46110 |
累积存水量 | m3 | 2211 | 4651 | 6793 | 9801 | 7434 |
累计回采水率 | % | 71 | 73 | 75 | 75 | 86 |
| [1] | 吴婷婷, 张风义, 王大为等. 渤海稠油油藏分类方法及分类界限研究 [J]. 新疆石油天然气, 2019, 15(3): 64-69. |
| [2] | 李廷礼, 张墨, 吴婷婷等. 渤海不同类型稠油油藏开发策略研究 [J]. 天然气与石油, 2023, 41(6): 110-116. |
| [3] | 孙鹏宵, 刘英宪. 渤海稠油油藏开发现状及热采开发难点与对策 [J]. 中国海上油气, 2023, 35(2): 85-92. |
| [4] | 孙福街. 中国海上油田高效开发与提高采收率技术现状及展望 [J]. 中国海上油气, 2023, 35(5): 91-99. |
| [5] | 张健, 李宜强, 李先杰等. 渤海油田非连续化学驱提高采收率机理 [J]. 石油学报, 2021-4-18, 网络首发. |
| [6] | 刘小鸿, 张风义, 黄 凯等. 南堡35-2海上稠油油田热采初探 [J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2011, 1(1-2): 61-63, 77. |
| [7] | 石飞, 常涛, 吴君达等. 海上多元热流体吞吐合理注采参数优化研究 [J]. 石油化工应用, 2023, 42(6): 49-52. |
| [8] | 刘东, 廖辉, 冯海潮等. 渤海稠油油藏水驱后转热水驱物模实验及应用 [J]. 中国海上油气, 2023, 35(2): 101-110. |
| [9] | 刘义刚, 张伟, 邹剑等. 海上稠油油藏热稀油复合吞吐解堵工艺技术研究 [J]. 山东石油化工学院学报, 2023, 31(4): 48-52. |
| [10] | 方涛, 刘义刚, 白健华等. 海上电潜泵井空心杆电加热工艺技术研究 [J]. 中国海上油气, 2023, 35(2): 163-167. |
| [11] | 苏彦春, 郑伟, 杨仁锋等. 海上稠油油田热采开发现状与展望 [J]. 中国海上油气2023, 35(5): 100-106. |
| [12] | 刘文章. 我国深井蒸汽吞吐采油试验 [J]. 石油钻采工艺, 1986(2): 59-64. |
| [13] | 顾浩, 孙建芳, 秦学杰等. 稠油热采不同开发技术潜力评价 [J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2018, 25(3): 112-116. |
| [14] | 姜得英. 稠油水平井蒸汽吞吐开发实践 [J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量, 2023, 6: 103-105. |
| [15] | 刘义刚, 钟立国, 刘建斌等. LD27-2油田稠油油藏蒸汽吞吐中后期注采参数优化研究 [J]. 能源与环保, 2020, 42(8): 86-91, 108. |
| [16] | 郑伟, 张利军, 朱国金, 等. 渤海油田稠油水平井蒸汽吞吐开发效果分析 [J]. 石油地质与工程, 2019, 33(4): 80-82, 87. |
| [17] | 刘东东, 张启龙, 翁昊阳等. 渤海油田稳产增产钻完井技术进展与展望 [J]. 天然气与石油, 2024-03-21, 网络首发. |
| [18] | 黄琴, 蔡晖, 桑丹等. 海上稠油油田水平井多轮蒸汽吞吐生产规律研究 [J]. 非常规油气2023, 10(2): 73-79. |
| [19] | 张锐等. 稠油热采技术 [M]. 北京:石油工业出版社, 1999. 4: 303-305. |
| [20] | 石乔木, 李韬, 董晓玲等. 扶余油田不同开发方式原油性质的变化 [J]. 石油知识, 2018, 1: 45-47. |
APA Style
Chai, S., Lian, Z., Zheng, J., Li, E. (2024). Evaluation of the Pilot Test Effect of Steam Stimulation in Horizontal Wells of Sand Bodies 1-1308 in Bohai L Oilfield. Science Discovery, 12(3), 54-57. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.sd.20241203.13
ACS Style
Chai, S.; Lian, Z.; Zheng, J.; Li, E. Evaluation of the Pilot Test Effect of Steam Stimulation in Horizontal Wells of Sand Bodies 1-1308 in Bohai L Oilfield. Sci. Discov. 2024, 12(3), 54-57. doi: 10.11648/j.sd.20241203.13
AMA Style
Chai S, Lian Z, Zheng J, Li E. Evaluation of the Pilot Test Effect of Steam Stimulation in Horizontal Wells of Sand Bodies 1-1308 in Bohai L Oilfield. Sci Discov. 2024;12(3):54-57. doi: 10.11648/j.sd.20241203.13
@article{10.11648/j.sd.20241203.13,
author = {Shichao Chai and Zhengxin Lian and Jianjun Zheng and Enlin Li},
title = {Evaluation of the Pilot Test Effect of Steam Stimulation in Horizontal Wells of Sand Bodies 1-1308 in Bohai L Oilfield
},
journal = {Science Discovery},
volume = {12},
number = {3},
pages = {54-57},
doi = {10.11648/j.sd.20241203.13},
url = {https://doi.org/10.11648/j.sd.20241203.13},
eprint = {https://article.sciencepublishinggroup.com/pdf/10.11648.j.sd.20241203.13},
abstract = {In order to reduce the risk of large-scale thermal recovery of heavy oil in Bohai Oilfield, L Oilfield is selected to carry out horizontal well steam stimulation pilot tests. Previous studies have summarized the rationality of the injection parameters and initial production characteristics of this experiment, but the evaluation of its development effectiveness is still blank. Based on the study of the decline law of A23H well cold recovery using reservoir engineering methods, this article evaluates the initial production capacity, production increase effect, technical recoverable reserves, and throughput cycles of steam stimulation. The results show that the thermal recovery production of steam stimulation is three times that of cold recovery, which can significantly improve the production capacity of a single well. The initial daily oil production of two wells is 74m3/d and 90m3/d, respectively, which is 3.0 times and 3.6 times that of the initial production of cold recovery, exceeding the design level of the reservoir; The first round has the best yield increase effect, with an average daily oil increase of 31m3/d, and gradually decreasing thereafter. By the fifth round, it was only 13m3/d. In terms of yield increase multiples, each round can reach about 2 times; The technically recoverable reserves are 19.03 × 104m3, requiring 8-9 rounds. Through this performance evaluation, we have strengthened our confidence in promoting the application of steam injection technology in Bohai Oilfield to achieve large-scale thermal recovery.
},
year = {2024}
}
TY - JOUR T1 - Evaluation of the Pilot Test Effect of Steam Stimulation in Horizontal Wells of Sand Bodies 1-1308 in Bohai L Oilfield AU - Shichao Chai AU - Zhengxin Lian AU - Jianjun Zheng AU - Enlin Li Y1 - 2024/06/19 PY - 2024 N1 - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.sd.20241203.13 DO - 10.11648/j.sd.20241203.13 T2 - Science Discovery JF - Science Discovery JO - Science Discovery SP - 54 EP - 57 PB - Science Publishing Group SN - 2331-0650 UR - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.sd.20241203.13 AB - In order to reduce the risk of large-scale thermal recovery of heavy oil in Bohai Oilfield, L Oilfield is selected to carry out horizontal well steam stimulation pilot tests. Previous studies have summarized the rationality of the injection parameters and initial production characteristics of this experiment, but the evaluation of its development effectiveness is still blank. Based on the study of the decline law of A23H well cold recovery using reservoir engineering methods, this article evaluates the initial production capacity, production increase effect, technical recoverable reserves, and throughput cycles of steam stimulation. The results show that the thermal recovery production of steam stimulation is three times that of cold recovery, which can significantly improve the production capacity of a single well. The initial daily oil production of two wells is 74m3/d and 90m3/d, respectively, which is 3.0 times and 3.6 times that of the initial production of cold recovery, exceeding the design level of the reservoir; The first round has the best yield increase effect, with an average daily oil increase of 31m3/d, and gradually decreasing thereafter. By the fifth round, it was only 13m3/d. In terms of yield increase multiples, each round can reach about 2 times; The technically recoverable reserves are 19.03 × 104m3, requiring 8-9 rounds. Through this performance evaluation, we have strengthened our confidence in promoting the application of steam injection technology in Bohai Oilfield to achieve large-scale thermal recovery. VL - 12 IS - 3 ER -