Objective To explore the diagnostic value and application effect of the combined detection of CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen), SCC (squamous cell carcinoma antigen), CYFRA21-1 (soluble fragment of cytokeratin 19), NSE (neuron specific enolase) and proGRP (gastrin releasing peptide precursor) in early lung cancer. Method 66 patients who admitted to the hospital from April 2019 to February 2024 were selected as the early stage lung cancer group and the other 159 patients were selected as the benign lung group, in which all subjects were tested for NSE, CEA, ProGRP, CYFRA21-1, and SCC levels and were confirmed by histopathological analysis. In ROC analysis, the cut-off point, AUC, accuracy, sensitivity and specificity between single and combined detection indicators are analyzed. Result The size of cut-off point, AUC, accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative detection rate and accuracy rate is 0.3072, 0.790, 89.33%, 0.894, 0.893, 89.40% (59/66), 89.31% (142/159) and 89.33% ((142+59)/225) respectively and it is obviously superior to those of single detection method. Meanwhile, indicator of SCC showed the worst performance by single detection. Conclusion The combined detection indicators have high diagnostic value in early diagnosis of lung cancer, and the sensitivity, positive detection rate, AUC value and accuracy have been significantly improved.
| Published in | Science Discovery (Volume 12, Issue 3) |
| DOI | 10.11648/j.sd.20241203.14 |
| Page(s) | 58-62 |
| Creative Commons |
This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, provided the original work is properly cited. |
| Copyright |
Copyright © The Author(s), 2024. Published by Science Publishing Group |
Combined Detection, Early Lung Cancer, Tumor Markers, Effectiveness Analysis
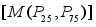 ,早期肺癌组用1表示,非肺癌组用0表示,考虑到对数据的研究是2分类问题,采用二元Logistic 回归获取组合检测指标,组间比较采用 Mann-Whitney U 检验,通过ROC曲线分析,我们可以研究5种肿瘤标志物作为单独及联合检测指标对早期肺癌组与非肺癌疾病组的敏感度、截断点、阳性/阴性检出率以及准确性AUC的诊断价值进行分析,以 P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
,早期肺癌组用1表示,非肺癌组用0表示,考虑到对数据的研究是2分类问题,采用二元Logistic 回归获取组合检测指标,组间比较采用 Mann-Whitney U 检验,通过ROC曲线分析,我们可以研究5种肿瘤标志物作为单独及联合检测指标对早期肺癌组与非肺癌疾病组的敏感度、截断点、阳性/阴性检出率以及准确性AUC的诊断价值进行分析,以 P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。 检测指标 | 分组 | 统计 | 自由度 | 显著性 |
SCC | 0 | 0.210 | 159 | .000 |
1 | 0.618 | 66 | .000 | |
proGRP | 0 | 0.955 | 159 | .101 |
1 | 0.287 | 66 | .000 | |
CEA | 0 | 0.638 | 159 | .000 |
1 | 0.285 | 66 | .000 | |
NSE | 0 | 0.694 | 159 | .000 |
1 | 0.606 | 66 | .000 | |
CYFRA21_1 | 0 | 0.464 | 159 | .000 |
1 | 0.426 | 66 | .000 |
指标 | 分组1:n = 99 |
| 分组0:n = 126 |
|
ProGRP (pg/mL) | 33.75 (27.73, 45.15) | 0.199 | 32.60 (23.55, 41.25) | 0.199 |
NSE (ng/ml) | 17.37 (13.08, 27.55) | 0.021 | 13.54 (11.69, 19.95) | 0.021 |
CEA (ng/ml) | 2.45 (1.47, 5.53) | 0.002 | 1.51 (1.10, 2.40) | 0.002 |
CYFRA21-1 (ng/ml) | 3.81 (2.50, 6.23) | 0.000 | 2.24 (1.60, 2.90) | 0.000 |
SCC (ng/mL) | 0.80 (0.50, 1.00) | 0.632 | 0.70 (0.55, 0.95) | 0.632 |
指标 | proGRP | NSE | CEA | CYFRA21-1 | SCC | 联合检测 |
截断值 | 98.200 | 15.1350 | 4.4000 | 2.41000 | 2.950 | 0.3072050 |
敏感度 | 0.091 | 0.621 | 0.303 | 0.773 | 0.091 | 0.894 |
特异度 | 1.000 | 0.610 | 0.943 | 0.522 | 0.943 | 0.893 |
约登指数 | 0.090909 | 0.231275 | 0.246427 | 0.29474 | 0.034305 | 0.787021 |
AUC值 | 0.576 | 0.636 | 0.685 | 0.775 | 0.528 | 0.829 |
P值 | 0.199>0.05 | 0.021<0.05 | 0.002<0.05 | 0.000<0.05 | 0.632>0.05 | 0.000<0.05 |
阳性预测值 | 9.01% (6/66) | 62.12% (41/66) | 30.3% (20/66) | 77.27% (51/66) | 9.01% (6/66) | 89.39% (59/66) |
阴性预测值 | 100% (159/159) | 61.01% (97/159) | 94.34% (150/159) | 52.20% (83/159) | 94.34% (150/159) | 89.31% (142/159) |
准确性 | 73.33% (165/225) | 61.33% (138/225) | 75.56% (170/225) | 59.56% (134/225) | 69.33% (156/225) | 89.33% (201/225) |
| [1] | Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021, 71: 209–49. |
| [2] | Bade BC, Dela Cruz CS. Lung cancer 2020: epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin Chest Med 2020, 41: 1–24. |
| [3] | Asakura K, Kadota T, Matsuzaki J, Yoshida Y, Yamamoto Y, Nakagawa K, Takizawa S, Aoki Y, Nakamura E, Miura J, Sakamoto H, Kato K, Watanabe SI, Ochiya T. A miRNA-based diagnostic model predicts resectable lung cancer in humans with high accuracy. Commun Biol, 2020, 3: 134. |
| [4] | 郑荣寿, 孙可欣, 张思维, 等. 2015 年中国恶性肿瘤流行情况分析 [J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2019, 41(1): 19-28. |
| [5] | Yanan Luo, Hui Yuan, Qin Pei, Yiyu Chen, Jiawen Xian, Rongrong Du and Ting Ye. Artificial neural network–based diagnostic models for lung cancer combining conventional indicators with tumor markers. Experimental Biology and Medicine 2023; 248: 829-838. |
| [6] | 许巧云. 探讨血清肿瘤标志ProGRP、NSE、CEA、CYFRA21-1、SCC单独及联合检测在肺癌鉴别诊断中的临床应用价值 [J]. 系统医, 2022, 7(03): 56-59. |
| [7] | 石岩. CYFRA21-1、ProGRP、SCC-Ag联合检测对肺癌的诊断价值 [J]. 临床医学研究与实践, 2021, 6(08): 46-48. |
| [8] | 凌云志,沈益青. CEA、SCC-Ag、CYFRA21-1联合检测对非小细胞肺癌的临床诊断价值 [J].国际检验医学杂志, 2021, 42(02): 231-234. |
| [9] | 王茜,夏睿,董惠霞等. ProGRP、NSE、CEA、CYFRA21-1、SCC单独及联合检测在肺癌鉴别诊断中的价值 [J].临床检验杂志, 2020, 38 (12): 930-932. |
| [10] | 邵莹,张强,翁文娟,赵明明.血清肿瘤标志物联合检测在肺癌诊断及分型中的价值 [J]. 牡丹江医学院学报, 2022, 43(02): 25-28+32. |
| [11] | 陈怡彤,张琳,王彦云, 哈敏文. 单独与联合检测四项肺癌血清肿瘤标志物在肺癌诊断中的价值分析 [J].中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2020, 27(S1): 56-57. |
| [12] | 许建林, 梁晓燕, 南永刚, 等. 肿瘤标志物联合检测对中老年肺结核合并肺癌的诊断价值研究 [J]. 海南医学院学报, 2016, 22(14): 1569-1572. |
| [13] | 刘亚婷,孙泰,宁芬,等. 血清肿瘤标志物单独和联合检测在小细胞肺癌分期中的临床价值 [J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘, 2019, 19 (44): 171-172. |
| [14] | 张辉. 单独与联合检测四项肺癌血清肿瘤标志物在肺癌诊断中的价值 [J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2018, 25(S2): 42-43. |
| [15] | 刘俊,孙璀. 血清肿瘤标志物单独或联合检测在原发性肺癌中的诊断价值 [J]. 检验医学与临床, 2017, 14(19): 2887-2889. |
| [16] | Soria J C, Le Chevalier T. Is cisplatin still the best platinum compound in non-small-cell lung cancer [J]. Annals of Oncology Official Journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology, 2002, 13(10): 1515. |
| [17] | 奚小祥, 吕 必宏, 叶婷等. NSE、Cyfra21-1、CEA及CA125 在孤立性肺结节诊断中的价值 [J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2015, 19(21): 41-43, 51. |
| [18] | Wu YL, Sun Y, Zhou CC, et al. Survival without common toxicity criteria grade 3/4 toxicity following second-linetreatment with pemetrexed for non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer in Chinese patient [J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2013, 126(24): 4624-4628. |
APA Style
Zhou, S., Ge, X., Yang, Z., Zeng, F. (2024). Effectiveness Analysis of the Combined Detection of CEA, SCC, CYFRA21-1, NSE and ProGRP for Early Diagnosis of Lung Cancer. Science Discovery, 12(3), 58-62. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.sd.20241203.14
ACS Style
Zhou, S.; Ge, X.; Yang, Z.; Zeng, F. Effectiveness Analysis of the Combined Detection of CEA, SCC, CYFRA21-1, NSE and ProGRP for Early Diagnosis of Lung Cancer. Sci. Discov. 2024, 12(3), 58-62. doi: 10.11648/j.sd.20241203.14
AMA Style
Zhou S, Ge X, Yang Z, Zeng F. Effectiveness Analysis of the Combined Detection of CEA, SCC, CYFRA21-1, NSE and ProGRP for Early Diagnosis of Lung Cancer. Sci Discov. 2024;12(3):58-62. doi: 10.11648/j.sd.20241203.14
@article{10.11648/j.sd.20241203.14,
author = {Shufang Zhou and Xiaojun Ge and Zhifang Yang and Fei Zeng},
title = {Effectiveness Analysis of the Combined Detection of CEA, SCC, CYFRA21-1, NSE and ProGRP for Early Diagnosis of Lung Cancer
},
journal = {Science Discovery},
volume = {12},
number = {3},
pages = {58-62},
doi = {10.11648/j.sd.20241203.14},
url = {https://doi.org/10.11648/j.sd.20241203.14},
eprint = {https://article.sciencepublishinggroup.com/pdf/10.11648.j.sd.20241203.14},
abstract = {Objective To explore the diagnostic value and application effect of the combined detection of CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen), SCC (squamous cell carcinoma antigen), CYFRA21-1 (soluble fragment of cytokeratin 19), NSE (neuron specific enolase) and proGRP (gastrin releasing peptide precursor) in early lung cancer. Method 66 patients who admitted to the hospital from April 2019 to February 2024 were selected as the early stage lung cancer group and the other 159 patients were selected as the benign lung group, in which all subjects were tested for NSE, CEA, ProGRP, CYFRA21-1, and SCC levels and were confirmed by histopathological analysis. In ROC analysis, the cut-off point, AUC, accuracy, sensitivity and specificity between single and combined detection indicators are analyzed. Result The size of cut-off point, AUC, accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative detection rate and accuracy rate is 0.3072, 0.790, 89.33%, 0.894, 0.893, 89.40% (59/66), 89.31% (142/159) and 89.33% ((142+59)/225) respectively and it is obviously superior to those of single detection method. Meanwhile, indicator of SCC showed the worst performance by single detection. Conclusion The combined detection indicators have high diagnostic value in early diagnosis of lung cancer, and the sensitivity, positive detection rate, AUC value and accuracy have been significantly improved.
},
year = {2024}
}
TY - JOUR T1 - Effectiveness Analysis of the Combined Detection of CEA, SCC, CYFRA21-1, NSE and ProGRP for Early Diagnosis of Lung Cancer AU - Shufang Zhou AU - Xiaojun Ge AU - Zhifang Yang AU - Fei Zeng Y1 - 2024/06/19 PY - 2024 N1 - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.sd.20241203.14 DO - 10.11648/j.sd.20241203.14 T2 - Science Discovery JF - Science Discovery JO - Science Discovery SP - 58 EP - 62 PB - Science Publishing Group SN - 2331-0650 UR - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.sd.20241203.14 AB - Objective To explore the diagnostic value and application effect of the combined detection of CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen), SCC (squamous cell carcinoma antigen), CYFRA21-1 (soluble fragment of cytokeratin 19), NSE (neuron specific enolase) and proGRP (gastrin releasing peptide precursor) in early lung cancer. Method 66 patients who admitted to the hospital from April 2019 to February 2024 were selected as the early stage lung cancer group and the other 159 patients were selected as the benign lung group, in which all subjects were tested for NSE, CEA, ProGRP, CYFRA21-1, and SCC levels and were confirmed by histopathological analysis. In ROC analysis, the cut-off point, AUC, accuracy, sensitivity and specificity between single and combined detection indicators are analyzed. Result The size of cut-off point, AUC, accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative detection rate and accuracy rate is 0.3072, 0.790, 89.33%, 0.894, 0.893, 89.40% (59/66), 89.31% (142/159) and 89.33% ((142+59)/225) respectively and it is obviously superior to those of single detection method. Meanwhile, indicator of SCC showed the worst performance by single detection. Conclusion The combined detection indicators have high diagnostic value in early diagnosis of lung cancer, and the sensitivity, positive detection rate, AUC value and accuracy have been significantly improved. VL - 12 IS - 3 ER -